Part 1: Establishing a Robust Reliability Compliance Program
Understand how the energy industry is embracing NERC standards for a secure Bulk Electric System (BES). Discover the fundamental elements of an effective compliance program, including organizational structure, culture of compliance, and more.
In the ever-evolving landscape of the energy industry, the North America Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC) regulatory standards have emerged as crucial benchmarks for ensuring the reliability and security of the Bulk Electric System (BES). Since their implementation in 2007, NERC standards have introduced a series of compliance obligations for various industry entities.
Our last article introduced us to NERC Compliance Management & Challenges. Need a moment to catch up? Give it a quick read!

In this article, we will delve into the fundamental tenets of an industry “best practice” NERC Reliability Compliance Program (RCP) or otherwise known as a NERC Internal Compliance Program (ICP) and describe an appropriate Organizational Structure for Electric Utilities to manage such a compliance program. More importantly, this article aims to provide guidance to Electric Utilities develop a robust Compliance Program designed to instill the necessary compliance culture and priority mindset throughout their organizations that will help assure an ongoing pro-active compliance posture.
Building the Foundation
A well-structured RCP or ICP encompasses the following fundamental elements:
- Organizational Structure: A clear hierarchy outlining roles and responsibilities
- Program Review and Oversight: Continuous monitoring and improvement.
- Compliance Assessment Processes: Procedures to evaluate compliance.
- Tracking of Requirements: Keeping up with evolving standards.
- Self-Reporting of Breaches: A transparent process for reporting violations.
- Mitigation Planning: Strategies to address non-compliance.
- Implementation Tracking: Processes to track implementation progress.
- Reliability Standard Management: Keeping abreast of standard changes.
- Training: Equipping personnel with the necessary knowledge.
- Employee Conduct-Culture of Compliance: Fostering a mindset prioritizing compliance.
- Continuous Improvement: Evolving to meet new challenges.
- Audits: Regular internal and external evaluations.
Creating a Culture of Compliance
For an RCP to be effective and sustainable, it should be endorsed across all levels of the organization. It must have suitable corporate level priorities established akin to safety and specific performance metrics for Senior Management to aid in fostering a culture of compliance and ensuring appropriate resources are made available for the program.
An RCP Policy is necessary and should be designed to develop and strengthen the culture of compliance within an organization from Senior Management down to the shop floor.
The Organizational Structure
The cornerstone of a successful and enduring RCP, which accomplishes the mentioned goals and effectively puts into practice the essential elements of a robust RCP, lies in its comprehensive organizational structure for ensuring reliability compliance. A sample of such an organizational structure is presented below:
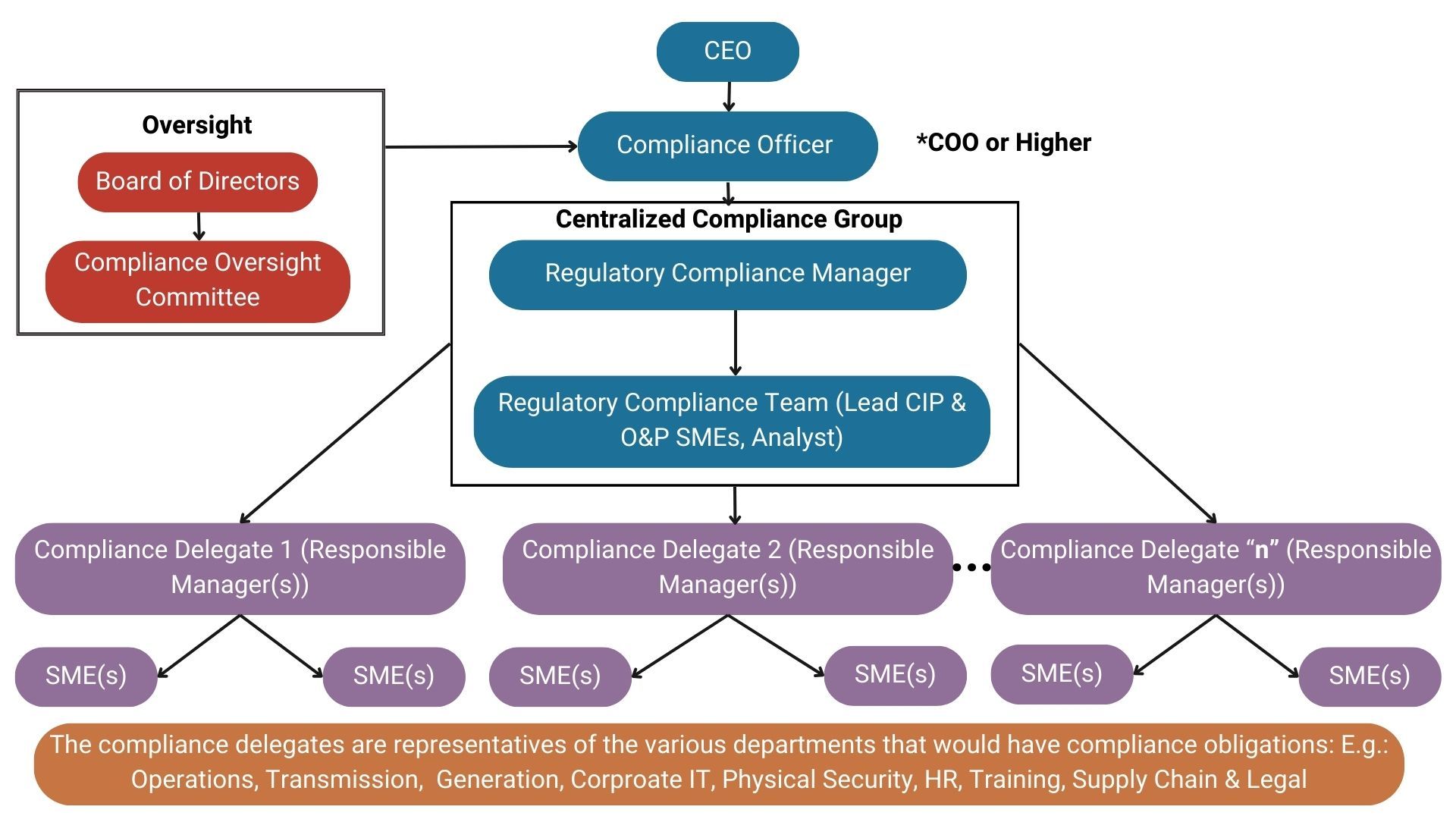
This example illustrates a suitable organizational structure that begins with top senior management supporting and fostering a strong culture of compliance and ends with all personnel working towards achieving and maintaining a robust compliance posture. Involving all staff in the endeavor to establish and sustain a robust compliance stance is fundamental to having an effective and sustainable Reliability Compliance Program.
It's important to acknowledge that the outlined organizational structure serves as just one model, and its suitability may vary depending on an entity's size and level of compliance exposure.
The Centralized Internal Compliance Group
The key group in the organizational structure is the centralized internal compliance group responsible to manage the compliance obligations, which includes but not limited to the following:
- Participate in the NERC and regional (RRO) meetings along with key SMEs, where appropriate.
- Ensure that the entity, where appropriate, has SMEs participates on NERC Standards drafting teams.
- Coordinate the provision of comments on new standards being developed or standards changes.
- Vote on new standards and changes to existing standards
- Stay on top of the standards as new standards are issued, existing standards revised, and some standards retired.
- Interpret the standards to ensure a consistent interpretation across all internal business units.
- Implement and manage Internal Controls
- Develop the required documentation, policies, procedures, programs, plans, processes, workflows and RSAWs.
- Ensure that the necessary evidence is captured to demonstrate compliance.
- Provide the necessary training to the staff, on the applicable NERC standards and associated requirements.
- Manage self-certifications, self-reports, and regional audits.
Typically, the staff and responsibilities of a NERC regulatory compliance group are usually situated within an organization such as the “Regulatory Affairs Department”. The industry’s experience and collective wisdom has shown that a fundamental tenet of a good compliance program is:
Those who manage and oversee regulatory compliance obligations should themselves not have any direct compliance obligations, so as to not introduce any ethical or conflict of interest dilemmas for reporting potential violations.
The NERC centralized compliance group should be made up of personnel with electric utility experience in the various functional areas with NERC obligations (e.g., Operations & Planning, Protection Systems, Cyber Security, etc.) who have strong electric industry knowledge and a good understanding of the NERC CIP and O&P requirements.
For more guidance on establishing a Robust Reliability Compliance Program, give our Acumen Whitepaper a read! Download and access the file below to dive more into this topic.
To give you more insights into these challenges, Acumen has prepared the following series of blogs that provides insight into an overall NERC compliance framework to support a robust internal compliance program.
Exploring Your Options
For the entities that have challenges in managing their NERC compliance obligations, Acumen offers the following services:
- Ad-Hoc NERC compliance services
- Fully or Partial NERC compliance managed services
For more information, visit www.aesi-inc.com or to schedule a complimentary consultation with us, book below!






